Goal: Unspecified.
Source: Unspecified.
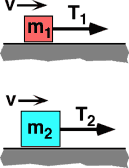
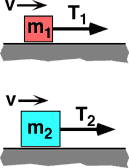
Two blocks with mass m2>m1 sit on a horizontal surface having friction. Both blocks are pulled with a constant speed, but v2 < v1, by a rope under tension. Which tension does the most work moving the block a distance D along the
surface?
- T1
- T2
- Both do the same work.
- Cannot be determined.

Commentary:
None provided.